Is the electromagnetic radiation of base stations terrifying?
What is electromagnetic radiation
When we talk about electromagnetic waves, we are talking about how much convenience they bring to our lives, especially in the era of 5G and the Internet of Things. Our phones, computers, iPads, and children's watches are the best examples of electromagnetic wave applications and the closest electromagnetic wave to us. However, when electromagnetic waves are given a new name, everyone may feel uneasy. In fact, electromagnetic waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. The term 'radiation' is particularly prominent. Students who have watched the American TV drama "Chernobyl" must be afraid of the enormous harm caused by nuclear radiation.
Ionizing and non ionizing electromagnetic radiation are two types of electromagnetic radiation that exist. Generalized electromagnetic radiation covers a large frequency range and wavelength distribution, ranging from tens of meters of long wave radiation to a few angstroms of gamma rays. Examples include radio waves and microwaves used for television transmission and wireless communication, as well as ultraviolet, infrared, visible, X-ray, and gamma rays. Ionizing radiation can extract electrons from atoms of an object, alter its chemical structure, and cause direct damage to cells in biological matter, while non ionizing radiation cannot. Ionizing radiation includes ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma rays. Fortunately, the radio waves and visible light that we are most exposed to in our daily lives are non ionizing radiation, which causes less harm to human health. However, we cannot turn a blind eye to what is happening.
What are the health hazards of mobile phone radiation?
As shown in the following figure, the article "Mobile phones: The Avengers of Modern People?" provides a detailed introduction to the forms of harm caused by electromagnetic radiation from mobile phones to the human body:
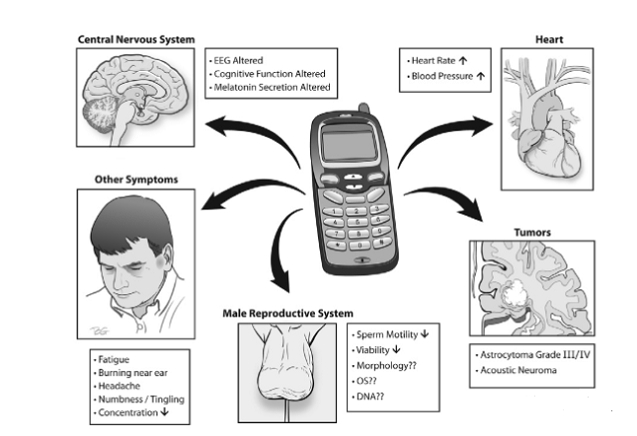
Damage to the cardiovascular system.
In a 1998 experiment, Braun et al. exposed human volunteers to RF-EMW at 900MHz for 35 minutes and found an increase in blood pressure (systolic and diastolic). Due to vascular failure, blood pressure increased by 5 ° 10 mmHg, while capillary perfusion significantly decreased.
Harms to sleep
Although Huber and others did not find any significant changes in sleep quality in an experiment conducted in 2000, exposure to 900MHz electromagnetic radiation for 30 minutes significantly increased the time to fall asleep and led to long-term insomnia.
Affects neurohormone secretion
Increase the likelihood of developing cancer
One of them is the carcinogenic potential of mobile phone radiation, which is the subject of extensive research conducted by various organizations. Hardell et al. (2006) conducted a study based on an epidemiological survey questionnaire to respond to public concerns that mobile phone exposure may lead to cancer, and found that astrocytoma (III-IV grade) and acoustic neuroma were indeed positively correlated with mobile phone use.
One patient had multiple breast cancer. This is strange because she has never had cancer. Although this possibility still exists, her doctor observed an unusual pattern in her cancer cells. I carefully examined it and found that it was the outline of her phone. They are confused about this. On the other hand, the woman claimed that she often stuffed her phone into her bra. Therefore, they will be able to connect her phone to the point between cancer cells.
Impact on male fertility
Many reports on the impact of mobile phone electromagnetic radiation on the male reproductive system still need to be clarified. But do you think you have the ability to conduct this experiment? In 2009, a study was conducted on 150 men who had their phones tied to their belts for a long time. Scientists have found that the pelvic bone density on the side of these men carrying mobile phones is lower.
Why is the weaker the signal, the greater the radiation of the phone?
Why can't our phones communicate wirelessly? The fundamental reason for doing this is that your phone can communicate with the base station, which then sends your signal to the phone you want to make a call.
The downlink signal sent by the mobile base station to your phone and the uplink signal sent by the phone to the mobile base station are two types of electromagnetic radiation involved here. In other words, when we make phone calls, we are exposed to two types of electromagnetic radiation: radiation from base stations and radiation from mobile phones. Everyone may be more concerned about the radiation of base stations, so many incidents have occurred where base stations have been dismantled in the community. After all, life and health are the most important considerations. When I saw the object above my head, I was scared.
First of all, let's
Firstly, let's discuss the radiation of base stations. The average power of a single channel in a modern 5G base station is approximately 5 watts, which is 320 watts or approximately 55 dBm across 64 channels. However, due to the electromagnetic wave path loss being equal to the square of the distance,
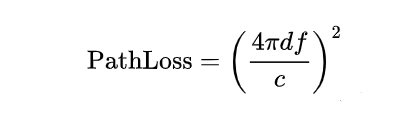
The distance is d, the frequency is f, and the speed of light is c. The path loss is proportional to the distance and frequency traveled.
Using the routing loss model above, let's take a look at how much radiation a 5G base station running on 2.6G emits to us under perfect conditions. Based solely on free space path loss, the following are the optimal power values. We can observe that even if the distance between the base station and the human body is only 10 meters, only 0.2 milliwatts of base station radiation reaches the human body.
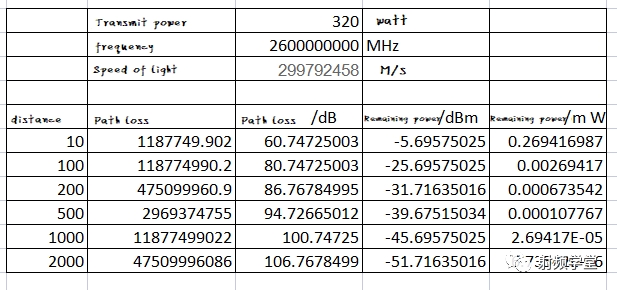
In fact, 5G base stations emit much less radiation to the human body. According to China Telecom, the power and radiation of 5G base stations are essentially low and within the national security parameters. Within a 10 meter range of a 5G base station, the current observed radiation is 1-1.5 μ W/cm。
However, due to the short distance, the impact of mobile phones on the human body is much greater. Currently, many people wear their phones on their bodies at any time and anywhere. According to the current 5G mobile phone transmission power standard, the power level 3 in the Sub6G spectrum is 23dBm; Power level 2 is 26dBm; Power level 1, with a higher potential power, according to the definition of 3GPP, there is currently no specification. At present, the commercial use of 5G is mainly focused on eMBB services provided by mobile phones running in the Sub6G frequency band. The following will mainly focus on this scenario, dividing the mainstream 5G frequency band into six categories (such as FDD n1, n3, n8, etc., as well as TDD n41, n77, n78, etc.). Explain this.
5G FDD (SA mode): The maximum transmission power is level 3, which is 23dBm;
5G TDD (SA mode): The maximum transmission power is level 2, which is 26dBm;
5G FDD+5G TDD CA (SA mode): maximum transmission power is level 3, 23dBm;
5G TDD+5G TDD CA (SA mode): maximum transmission power is level 3, 23dBm;
4G FDD+5G TDD DC (NSA mode): maximum transmission power is level 3, 23dBm;
4G TDD+5G TDD DC (NSA mode): The maximum transmission power defined by R15 is level 3, which is 23dBm, while the maximum transmission power supported by R16 version is level 2, which is 26dBm.
That is to say, the worse the signal of a mobile phone, the more power it must transmit, and the purpose of communication with the base station has been achieved. This means that when the signal is weak, your phone will use full power, approximately 26dBm, or 398 milliwatts, which is almost 1000 times the radiation of a 10 meter base station. According to telecommunications testing, the standby radiation value of the mobile phone is about 17.1 microwatts/square centimeter, and it is about 93.1 microwatts/cubic centimeter during calls. The worse the signal during a call, the higher the radiation level, and the farther the phone is from the base station. So, if you're really scared, instead of destroying the base station, it's better to break your phone.
However, please rest assured that even if the power of the phone increases, its radiation remains within an acceptable range. Many professionals in the local communication industry have stated that China's mobile communication base station radiation requirements comply with IEC, EU, and US standards; However, Japan's regulations are 12 to 15 times higher. The reason is that choosing a base station in the aforementioned countries and regions is extremely challenging. The base station provides a wide coverage range and high transmission power. According to the radiation standards for mobile communication base stations released by various countries, the United States and Japan have a radiation standard of 600 microwatts per square centimeter, the European Union has a radiation standard of 450 microwatts per square centimeter, and China has a radiation standard of 40 microwatts per square centimeter.
In fact, the radiation of the base station is significantly lower than the requirements of China and the standards of Europe and the United States. At the same time, the density of 5G base stations is higher, the transmission power is lower, the frequency is higher, and the propagation loss of each base station increases. According to actual measurements, the radiation observed within a 10 meter range of a 5G base station is approximately 1-1.5 microwatts per square centimeter. For terminals close to the base station, the transmission power will be adaptively reduced.
Moreover, the radiation level of the base station is lower than that of many common household devices. A microwave oven with a relatively high radiation dose emits 268 microwatts per square centimeter within a distance of 1 meter, but China's base station radiation standard only emits 1/6 of the microwave oven radiation.
Therefore, basic base stations are not scary. More consideration should be given to the radiation sources around us
- Prev:What is an RF filter?
- Next:None
-
Whatsapp

